Osteomyelitis - DRHC Dubai Pediatric Orthopedic Clinic
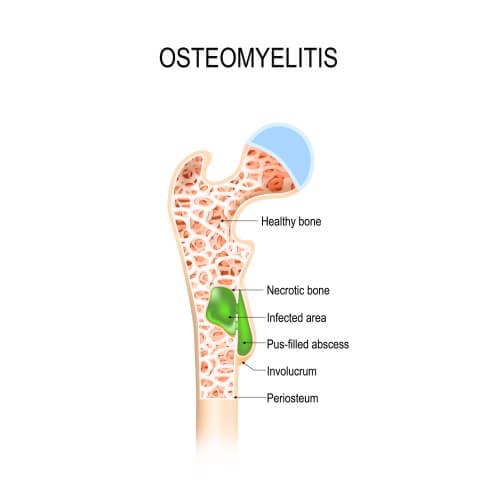
Osteomyelitis is not uncommon even in healthy children. Acute osteomyelitis typically occurs at the ends of the long bones (metaphyses) near the joints, as well as in the pelvis or spine, due to the rich metaphyseal blood supply and the immature immune system. These infections can arise from hematogenous seeding of bacteria (the most common cause) or from direct inoculation of bacteria across a skin defect.
Risk factors for osteomyelitis include:
- Trauma: 30% of osteomyelitis patients have experienced blunt trauma.
- Immune System Weakness: Conditions such as diabetes mellitus, chronic renal disease, hemoglobinopathy, and rheumatoid disease can weaken the immune system. Osteomyelitis is seen in children under the age of 3 years.
The common pathogenic bacteria associated with osteomyelitis are:
- Staph aureus (the most common organism)
- Group B Strep
- Pseudomonas
- H. influenza
- Salmonella (common in sickle cell patients)
In infants less than 1 year old, the infection can cross the growth plate and cause osteomyelitis in the epiphysis and septic arthritis in the adjacent joint.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
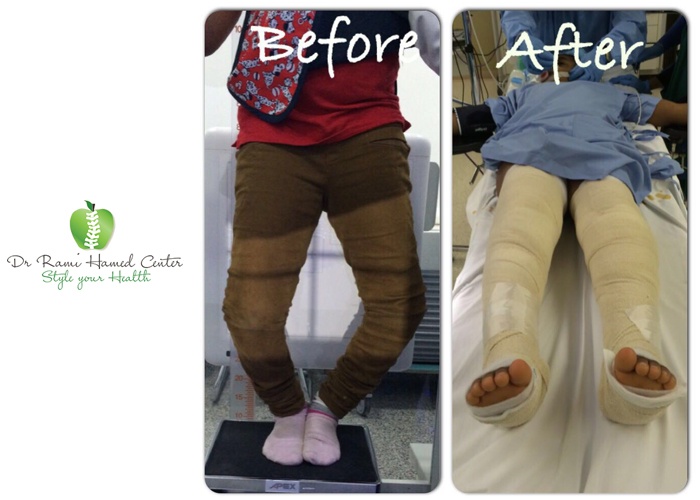
Children with osteomyelitis often present with fever, tenderness, edema, warmth, swollen limbs, pain, and an inability to bear weight on the affected limb. Sometimes, systemic symptoms such as irritability, lethargy, vomiting, and loss of appetite may also be present.
Diagnosis involves several tests:
- Imaging Tests: Early X-rays may be normal or show tissue edema. The formation of new periosteal bone around the infected bone can be detected after 7 days of the onset by a simple X-ray. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the preferred imaging method as it can detect marrow and soft tissue edema and abscess early. Its sensitivity is increased by Gadolinium contrast.
- Lab Studies: These will show a high blood count with elevated C-reactive protein and sedimentation rate.
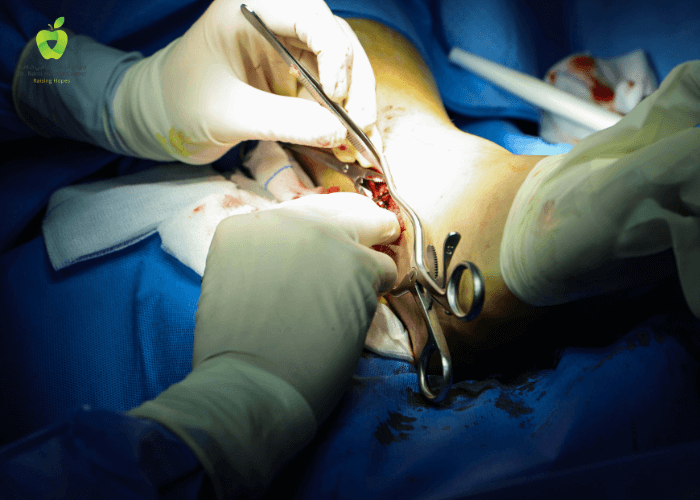
- Aspiration: Using a large bore needle, aspiration of the subperiosteal and intraosseous spaces is performed under fluoroscopic or CT-guidance. This is essential for diagnosis and guided antibiotic therapy.
Treatment Options
Treatment for osteomyelitis is typically urgent:
- Antibiotic Therapy: In the early stages of the infection without abscess formation, antibiotic therapy alone is used. If there is no improvement within 48 hours, surgical drainage, debridement of the infected bone, and subperiosteal abscess are performed, followed by continued antibiotic therapy.
.png?width=281&height=59&name=bookanappointment%20(1).png)
If you are in search of the best pediatric orthopedic surgeon in Dubai or a children's orthopedic specialist in Dubai, then DRHC Orthopedic Clinic in Dubai offers you the top pediatric orthopedic surgeons with vast years of experience. To book an appointment, call +97142798200. DRHC Dubai also offers a foot clinic with highly experienced foot specialists.



.png?width=281&height=59&name=bookanappointment%20(1).png)