CT-Scan Procedures:
- All Routine CT Plain & Contrast
- HRCT Chest (High Resolution CT)
- CT Angiography
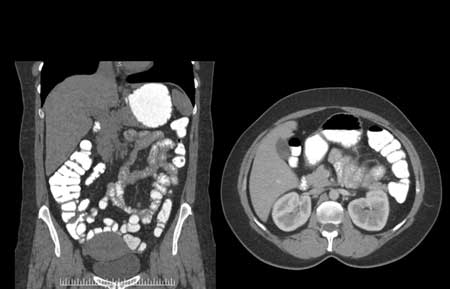
- CT Abdominal w/ Oral Contrast
- CT Abdomen Multiphase Contrast
- CT Stonogram/KUB
How does it work?
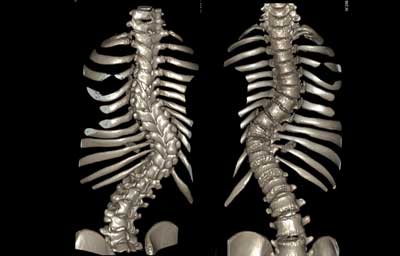
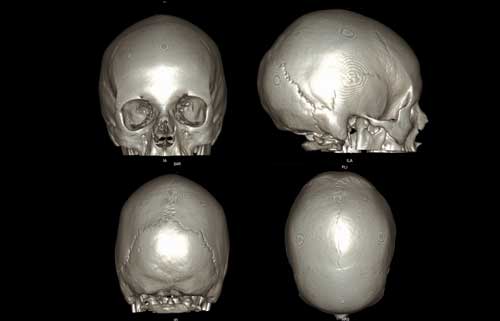
CT is the same as X-ray, just more complicated. With CT-scan, X-ray images are taken cross-sectionally in a round tube and not just in one or two images but multiple images ranging from 1-100 or more images in just a few seconds, and will be processed with the CT-computer system to produce viewable 2D and 3D images.
Who can have a CT scan?
- From Pediatrics to Adults and even Geriatrics, Male or Female, but for pregnant patients, it should be assessed properly by the referring doctor, if the benefits can outweigh the risks.
- Infants & Children
Infants and young children sometimes require sedation or anesthesia to complete a CT exam without moving. Whether a child requires sedation will depend on the child’s age and the type of exam being performed. Moderate and conscious sedation can be provided. A physician or nurse specializing in the administration of sedation or anesthesia to children should be available during the exam to ensure the child's safety. Special instructions will be given on how to prepare the child for the sedation or anesthesia.
Why CT-scan?
- A noninvasive way to study all parts of your body
- Less sensitive to movement than MRI
- Help doctors plan for and later assess the results of many surgeries.
- Its ability to image bone, soft tissue, and blood vessels all at the same time
- To further look at an abnormality seen on another test, such as an X-ray or an ultrasound
Risk:
- Use of Ionizing radiation
Routine Operating Procedure in CT-scan:
- The doctor’s request is reviewed by the staff radiographer.
- A safety questionnaire and a consent form are provided before the scan.
- Hospital gowns are provided if needed to avoid artifacts on images.
- Patient’s personal belongings (including phone, credit cards, money, etc.) are all placed in the locker provided.
- The radiographer will explain what will be the position & how much time it will take to complete the scan.
- The radiographer will ask the patient to lie on the scanner bed and will position the patient comfortably by placing pads or pillows.
- CT-scan exams are painless and fast. It is important that the patient remains perfectly still while the images are being recorded.
CT-scan with Contrast:
- Some CT examinations may require the patient to receive an injection of contrast material into the bloodstream or be orally given (also known as DYE).
- The patient will be instructed to fast before the procedure.
- The patient should let the radiographer know if they have any serious health problems or if they have had any recent surgeries. Some conditions, such as severe kidney disease or liver transplant, may prevent a patient from being given iodinated contrast.
- It will be necessary to perform a blood test (creatinine) to determine whether the kidneys are functioning adequately.
- The radiographer or a nurse will ask the patient if they have allergies of any kind, such as an allergy to drugs, food, or the environment, if they have asthma or diabetes, so that proper precautions will be made.
- The contrast material used for a CT exam is based on iodine. Through advancements in science, contrasts are made to have fewer allergic reactions, so even if it is known that the patient has an allergy, it may still be possible to use it after appropriate assessment or pre-medication.
- The radiographer will advise the patient to drink plenty of water after the injection of contrast for the next 24 hours to wash out the contrast from the system.
- Breastfeeding patients will be advised after the procedure when they can continue to breastfeed their infants after being assessed by the Doctor.
Related topics:
.png?width=281&height=59&name=bookanappointment%20(1).png)
To book an appointment, please call us at +97142798200 today!




.png?width=281&height=59&name=bookanappointment%20(1).png)


