Sleep Apnea - DRHC Dubai ENT Clinic DRHC
Make a general examination, looking for any craniofacial abnormalities.
- Listen carefully for stertor while awake or asleep.
- Watch for mouth breathing.
- Carry out an oral examination to determine the size of the tonsils.
These can be graded by 2 Methods:
The Brodsky score
- Tonsils in the fossa
- Tonsils occupy up to 25% of the airway
- 26% to 50%
- 51% to 75%
- more than 75%
The Friedman score
- No tonsils
- Tonsil within the pillars
- Tonsil beyond the pillars
- Tonsil extending to the midline
- Tonsils are touching in the midline.
- Examine the nose to establish whether there is coexisting rhinitis and whether there is likely to be adenoid hypertrophy.
- Examine the ears for coexisting otitis media with effusion.
- Look for neck lymphadenopathy
How to confirm the diagnosis of sleep apnea
- Oximetry overnight for observation of the O2 saturation and heart rate
- Polysomnography
- Nasolaryngoscopy
- Imaging for the airway and mandible
- Laboratory tests
How to manage sleep apnea
- Diet and exercise to reduce the bulky tissue around the airway passage
- Medicines for treating adenoids, allergy, GERD, etc.
- Adenoidectomy with or without tonsillectomy or tonsillotomy
- Jaw distraction in micrognathia (small mandible) or big tongue, etc.
- Oral appliance
- Tongue reduction if the tongue is big
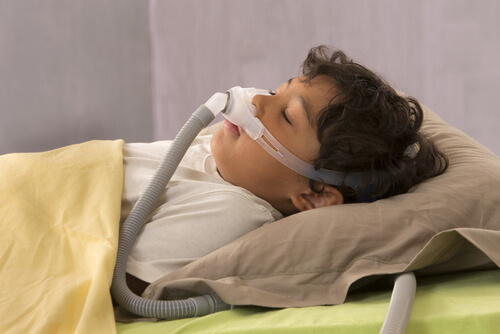
- Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) may be required in children where treatment is not possible.
Indications for Pediatric Respiratory Investigations
- Diagnosis of OSA is unclear or inconsistent
- Age <2 years
- Weight <15 kg
- Down syndrome
- Cerebral palsy
- Hypotonia or neuromuscular disorders
- Craniofacial anomalies
- Mucopolysaccharidosis
- Obesity (BMI >2.5 SDS (standard deviation scores),
- Significant comorbidities such as congenital heart disease,
- chronic lung disease
- Residual symptoms after adenotonsillectomy
Click here for ENT surgical packages
.png?width=281&height=59&name=bookanappointment%20(1).png)
Dubai ENT clinic - If you are in search of an ENT specialist in Dubai, then DRHC provides experienced and leading ENT doctors in Dubai for healthy treatment. To book your appointment, please call +97142798200 today!



.png?width=281&height=59&name=bookanappointment%20(1).png)
.jpg?width=1080&height=1080&name=DR%20HATEM%20(1).jpg)