Colon polyps at DRHC Dubai
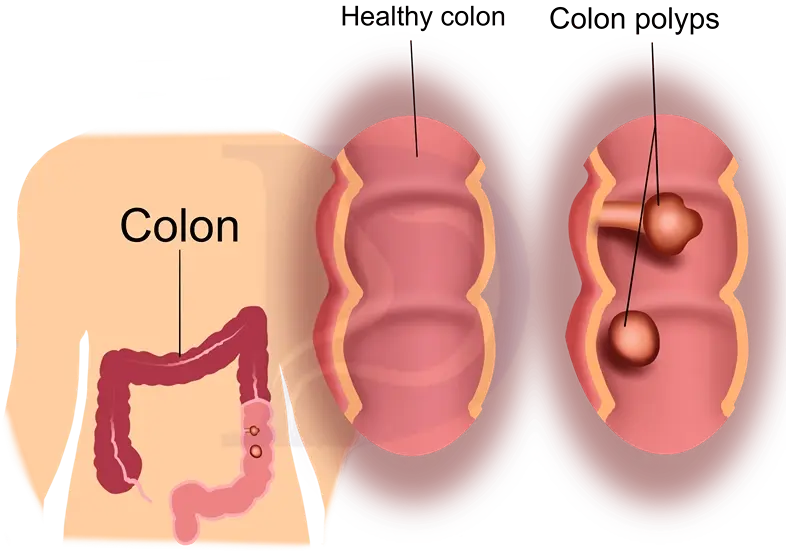
Colon polyps are abnormal growth of tissue that forms on the lining of the colon. It can develop somewhere else, for example, in the cervix or ears but the most common site is the colon. Anyone can develop polyps but at the age of 50, people are at higher risk. Most of the polyps are harmless but over time, they may become cancerous, and in their late stages, it is fatal.
Risk factors are smokers, overweight persons, heavy alcohol use, physical inactivity, family history, race (African-American), and Type 2 Diabetes not well controlled. There are two (2) types of polyps: Non-neoplastic and Neoplastic.
The Non-neoplastic are for example:
- Hyperplastic Polyps, which are small benign mucosal changes without a degeneration tendency (no development of cancer).
- Inflammatory Polyps are also benign and small, but with inflammatory changes.
- Hamartomas are disorganized growth of tissue that forms a polyplex structure but are not cancerous.
The Neoplastic type is adenomas or adenomatous polyps, for example:
- Familial Adenomatous Polyposis is an autosomal dominant inherited condition that causes the formation of many adenomatous polyps in the intestine. Although it starts as benign polyps if left untreated, malignant transformation can occur.
- Serrated Polyposis Syndrome is a pre-malignant lesion leading to colorectal cancer.
- Lynch Syndrome or Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer (HNPCC), is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder that has a high risk of malignancy. It is also associated with tumors in the stomach, breast, urine tract, uterus, and ovaries.
- Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder that causes the development of benign polyps accompanied by macules on the skin and oral mucosa.
Symptoms are either a coincidence during the Colonoscopy or because of rectal bleeding, a change in the stool color and bowel habit, anemia, and unexplained weight loss. Complications are usually rare, but anemia is especially due to chronic bleeding or obstruction and invagination.
Diagnosis is made either by a Routine Rectal Digital Examination with palpable tumor or bleeding, Proctoscopy and Colonoscopy with biopsy or removal of polyp, Fecal Immunochemical test, Guaiac-Based Fecal Occult Blood Test (G-FOBT), or CT Colonography.
Treatment is, in general, if possible, to remove during endoscopy. If the polyp is big and not possible to be removed during an endoscopy, then either through a colotomy, which is the opening of the colon with the removal of the polyp, or by performing a segment (partial) resection. If histopathology shows cancer, then surgery should be performed according to oncological criteria.
Prevention: Having a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise, diet (low in red meat), and not smoking is very helpful in preventing colon cancer. Additionally, stool test and screening (Colonoscopy) are always needed starting at the age of 50. Having a healthy lifestyle is not always easy, but it decreases the risk of many diseases. General knowledge and health awareness are 2 important factors. Early consultation with your doctor is really helpful.
For any questions, please don’t hesitate to contact us.
Click here for Proctology Surgery Packages
.png?width=281&height=59&name=bookanappointment%20(1).png)
The proctologist at the proctology clinic at our center provides the best diagnosis of hemorrhoids, hemorrhoid treatment, hemorrhoidectomy, and Laser Surgery for hemorrhoids. Call us at DRHC to book your appointment at +97142798200.



.png?width=281&height=59&name=bookanappointment%20(1).png)
.webp?width=1080&height=1080&name=Doctor%20background%20For%20Website%20Dr.%20Fadi%20Nageeb%2009%20(1).webp)
.webp?width=1080&height=1080&name=Doctor%20background%20For%20Website%20Dr%20Abdul%20Majeed%20Khalid%20%2002%20(1).webp)