Skin and Soft Tissue Infections - Dubai General Surgery Clinic DRHC
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
Soft tissue infections are very common reasons for presentation to outpatient clinics, hospitals, and even in emergency cases to the ICU. These infections include the skin, subcutaneous tissue, fascia, and muscle. It results from bacterial attacks on the skin and underlying structures. It may present itself as a simple, mild infection, such as pyoderma, or it can progress rapidly, causing necrotizing fasciitis. The infection can be classified as uncomplicated or complicated (with or without necrosis) or as suppurative or non-suppurative.
- Complicated infections may cause systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). The challenge is to be able to differentiate cases that require immediate consultation and intervention.
- The diagnostic criteria depend on the clinical manifestation of the inflammation, which may cause erythema, edema, hyperemia, pain, tenderness, and fever.
- The affected area may become dysfunctional depending on the severity, for example, the upper or lower extremities.
- Co-morbidities such as diabetes, cirrhosis, or AIDS may change a mild infection into a serious, life-threatening situation.
- Some of the differential diagnoses of skin and soft tissue infection are contact dermatitis, superficial thrombophlebitis (inflammation of the superficial veins), deep venous thrombosis (which leads to obstruction and inflammation), and drug reactions.
The diagnosis is based on clinical description and evaluation.
- Fluctuation,
- Necrosis,
- Crepitus (Crackling)
- Laboratory tests (High or low white blood cells, high levels of CRP (C-reactive protein), blood cultures, swab cultures, and needle aspiration)
- Ultrasound
- MRI/CT
Either the temperature is below 35 degrees Celsius or higher. Tachycardia, hypertension, and changes in mental status represent systemic toxicity, which causes sepsis or shock.
- The size and site of the infection are very important factors.
- Large and progressive infections require immediate management and intervention.
- Minor skin lesions can be treated with topical ointments (antibiotics), and simple skin infections or abscesses can be treated with incisions and drainage without antibiotics.
- Complicated abscesses need drainage with antibiotic therapy. Experienced physicians with advanced skills should be able to evaluate the severity of the infection.
- It may start as a simple dermatological issue. Nevertheless, surgical consultation is always advisable. The surgeon is the one who will indicate or decide if surgery is needed.
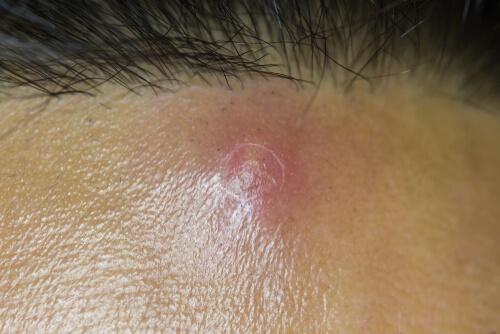
Sebaceous cyst:
A sebaceous cyst is a capsulated pump that includes sebum (an oily substance). A sebaceous cyst can develop when the opening of a sebaceous gland becomes obstructed.
- It is usually a painless, slow-growing swelling under the skin.
- It often appears on the scalp, face, trunk, back, or even the groin area.
- It is common in adults and rare in children.
Sebaceous cysts are a benign, noncancerous disease
It is characterized as a movable, rounded pump with a smooth surface, without pain (unless it gets inflamed), with a size ranging from millimeters to several centimetres. It is easily diagnosed by careful physical examination.
A sebaceous cyst generally does not require to be treated unless it is inflamed or is causing discomfort or a cosmetic problem.
An inflamed cyst is usually treated by incision and drainage of the fluid, and removal of the capsule if possible.
also treated with antibiotics if the skin around the sebaceous cyst is infected.
If a sebaceous cyst is causing discomfort or cosmetic disorder, excision of the sebaceous cyst is recommended by making a small incision in the skin over the cyst and removing the cyst and its wall.
.png?width=281&height=59&name=bookanappointment%20(1).png)
For any questions regarding this topic, please feel free to contact us at any time at +97142798200 / +971524830895



.png?width=281&height=59&name=bookanappointment%20(1).png)
.webp?width=1080&height=1080&name=Doctor%20background%20For%20Website%20Dr.%20Fadi%20Nageeb%2009%20(1).webp)
.webp?width=1080&height=1080&name=Doctor%20background%20For%20Website%20Dr%20Abdul%20Majeed%20Khalid%20%2002%20(1).webp)



