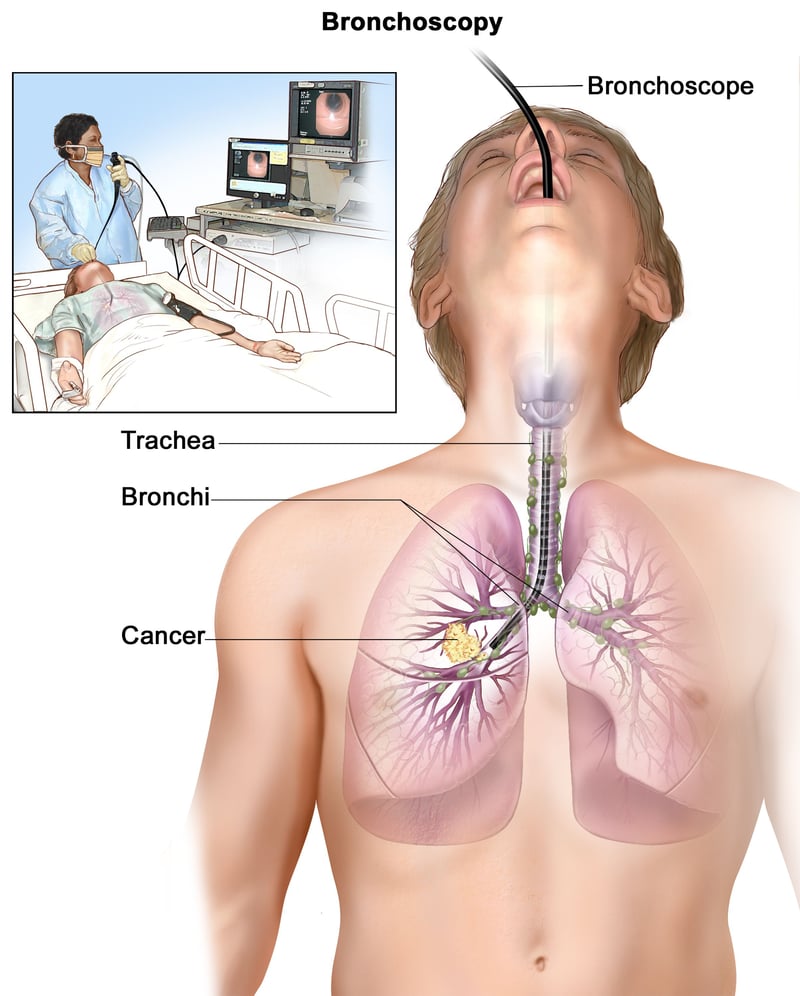
Bronchoscopy:
When it comes to bronchoscopy, the decision between a flexible or rigid approach depends on the specific case and the preferences of the surgeon, all in the interest of providing the best possible care for the patient. At DRHC Dubai, our expert thoracic surgeon will provide a detailed explanation of the procedure and ensure a smooth and successful bronchoscopy experience.
Flexible Bronchoscope
Utilizing local anesthesia, the flexible bronchoscope is primarily used for diagnostic purposes. Its interventions are limited to suctioning, making it a valuable tool for examining the airway and assisting with intubation. However, its airway control capabilities are also limited.
Indications:
- Airway obstruction
- Stridor
- Noisy breathing
- Snoring of uncertain anatomical origin
- Persistent or recurrent wheezing
- Evaluation of the artificial airway
- Aid in intubating the difficult upper airway
- Vocal cord paralysis
- Chronic cough
- Hemoptysis
- Suspected foreign body aspiration
- Atelectasis
- Recurrent/persistent consolidation
- Atypical and unknown infiltration
- Localized hyperinflation
Interventional Bronchoscopy Procedures:
- Performing biopsies on endobronchial lesions to obtain tissue samples for further analysis.
- Conducting brushing or biopsies of the bronchial mucosa to gather samples for diagnostic purposes.
- Administering bronchoalveolar lavage, a procedure where fluid is instilled into the lungs and then withdrawn to assess lung function and collect samples.
- Conducting transbronchial biopsies, which involve obtaining tissue samples from the lungs using a bronchoscope.
- Administering drugs through the bronchoscope for targeted treatment.
Contraindications:
- Avoiding the use of flexible bronchoscopy in non-intubated patients experiencing difficulty breathing.
- Not performing bronchoscopy in patients with coagulopathy, a condition that impairs blood clotting.
Risks:
While patient discomfort and transient hypoxemia are common, it may lead to a fever 4 to 12 hours post-procedure. More serious complications such as pneumonia, respiratory failure, life-threatening hemoptysis, pneumothorax, and death are rare.
Complications (6.9%):
- Minor complications (5.2%)
- Moderate and transient episodes of desaturation
- Excessive isolated coughing
- Excessive nausea reflex with coughing
- Transient laryngospasm
- Epistaxis
Major complications (1.7%)
- Oxygen desaturation to <90%, either isolated or associated with laryngospasm
- Coughing
- Bronchospasm
- Pneumothorax
- Transient fever after bronchoalveolar lavage
Rigid Bronchoscopy
- With general anesthesia and correct ventilatory support, the rigid bronchoscopy offers safe grasping with rigid forceps, quick removal, and blood suctioning. It is particularly useful for various indications, including bleeding or hemorrhage, foreign body extraction, mucus plugs or blood clots, defining anatomic details, and interventional bronchoscopy (laser, stents).
Contraindications:
- Relative contraindications include uncontrolled coagulopathy, critically ill patients requiring mechanical ventilation, acute laryngitis, and mandibular hypoplasia.
Risks:
- While the risks associated with rigid bronchoscopy include injury to the teeth or gums, tracheal or bronchial tears, and severe bleeding, the complication rates should be less than 0.1%. Procedure-related mortality is rare.
- For top-notch Thoracic surgery in Dubai, contact DRHC at +97142798200. We offer expert Thoracic surgeons and comprehensive care.