Osteochondritis Dissecans (OCD) at DRHC Dubai
What is Osteochondritis Dissecans (OCD)?
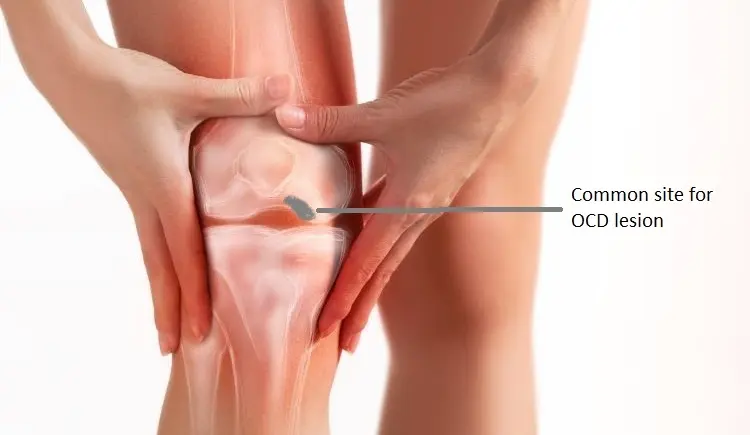
Osteochondritis Dissecans (OCD) is a joint condition that occurs when a small segment of bone and the overlying cartilage separate from the surrounding area due to a lack of blood supply. This can cause the bone and cartilage to crack or loosen, leading to pain, swelling, and, in severe cases, joint instability. OCD is most commonly seen in young athletes, particularly those involved in high-impact sports. The knee is the most frequently affected joint, but OCD can also occur in the elbow, ankle, and other joints.
At DRHC Dubai, our expert orthopedic team offers comprehensive care for sports-related OCD, helping athletes manage their symptoms, recover, and prevent further damage.
Causes of Osteochondritis Dissecans in Sports
The exact cause of OCD is not entirely understood, but repetitive stress and trauma are considered major contributing factors. In athletes, OCD often develops due to repeated impact or strain on the joint over time. Sports activities that put significant stress on the joints, such as running, jumping, or throwing, can increase the risk of developing OCD. Key causes include:
- Repetitive joint stress: Sports like soccer, basketball, and gymnastics place repetitive stress on the joints, especially the knees and elbows, increasing the likelihood of OCD.
- Trauma or injury: A direct blow to the joint or repeated microtrauma can lead to the separation of bone and cartilage, particularly in sports involving sudden stops, turns, or pivots.
- Genetics and growth factors: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to OCD, and the condition is more common in growing children and teenagers, especially those involved in competitive sports.
Symptoms of Osteochondritis Dissecans (OCD)
OCD symptoms vary depending on the severity of the condition and the joint affected. Athletes may experience:
- Pain: Joint pain that worsens with physical activity, especially high-impact movements like jumping or running.
- Swelling: Swelling around the affected joint, which may increase after activity or prolonged use.
- Locking or catching sensation: A feeling that the joint is “locking” or “catching” during movement, particularly when the loose bone fragment interferes with normal joint motion.
- Decreased range of motion: Athletes may notice stiffness or a reduced ability to fully move the affected joint.
- Joint instability: In severe cases, the joint may feel unstable or weak, particularly if the loose fragment moves around within the joint.
Diagnosis Osteochondritis Dissecans
Early diagnosis is critical to prevent further joint damage and ensure a successful recovery. At DRHC Dubai, we use a combination of methods to diagnose OCD, including:
- Physical Examination: The doctor will assess the joint for pain, swelling, and limited range of motion.
- X-rays: X-rays are often used to detect the presence of loose bone fragments and evaluate the extent of damage to the bone and cartilage.
- MRI or CT scans: Advanced imaging techniques such as MRI or CT scans may be recommended to provide a detailed view of the affected area, assess cartilage health, and determine the severity of the condition.
Treatment Options for Osteochondritis Dissecans
The treatment of OCD depends on the age of the patient, the severity of the condition, and the size and stability of the loose bone fragment. At DRHC Dubai, our orthopedic specialists provide both non-surgical and surgical treatments based on the needs of each patient:
Non-Surgical Treatment
For mild cases or younger athletes whose bones are still growing, non-surgical treatments may be effective. These include:
- Rest and activity modification: Avoiding high-impact activities that put stress on the affected joint is crucial for healing. Athletes may need to rest for several months to allow the bone to heal.
- Immobilization: In some cases, immobilizing the joint with a brace or cast may help stabilize the area and promote healing.
- Physical therapy: Once the initial pain and swelling subside, physical therapy is important to restore strength, flexibility, and range of motion to the affected joint. At DRHC Dubai, our rehabilitation programs are designed to help athletes safely return to sports after recovery.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery may be necessary for athletes with more severe OCD or when conservative treatments are not effective. Surgical options include:
- Arthroscopic surgery: This minimally invasive procedure is commonly used to remove or repair loose bone fragments. The surgeon makes small incisions and uses a camera to guide instruments to treat the damaged area.
- Drilling or microfracture: To encourage healing, the surgeon may drill small holes in the bone to stimulate blood flow to the damaged area and promote new bone growth.
- Bone grafting: In cases where the bone and cartilage have sustained significant damage, a bone graft may be required to restore the joint’s structure and function.
- Fixation of loose fragments: If the loose bone fragment is large and still viable, the surgeon may use pins or screws to reattach it to the surrounding bone.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
The recovery process for OCD varies depending on the severity of the condition and the type of treatment used. For athletes undergoing non-surgical treatment, recovery may take several months, while those requiring surgery may need a longer rehabilitation period. Rehabilitation focuses on:
- Restoring joint function: Physical therapy is a key part of the recovery process, helping athletes regain strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
- Gradual return to sports: Athletes are advised to gradually resume sports activities under the guidance of their doctor and physical therapist to avoid re-injury.
- Long-term joint health: Proper rehabilitation and ongoing strengthening exercises are essential to prevent future joint problems.
At DRHC Dubai, our dedicated sports medicine and orthopedic team works closely with each patient to ensure a full recovery and safe return to sports.
Preventing Osteochondritis Dissecans in Athletes
While it may not always be possible to prevent OCD, there are steps athletes can take to reduce their risk:
- Proper warm-up and cool-down: Engaging in dynamic warm-up exercises before sports activities and stretching afterward helps reduce joint stress.
- Strength training and conditioning: Building strong muscles around the joints provides additional support and reduces the risk of injury.
- Avoiding overuse: Limiting repetitive, high-impact activities can reduce the strain on growing bones and joints, especially in young athletes.
- Using proper technique: Learning the correct techniques for movements like jumping, running, and pivoting can help minimize the risk of joint injuries.
Why Choose DRHC Dubai for OCD Treatment?
At DRHC Dubai, we offer state-of-the-art orthopedic care for sports injuries, including Osteochondritis Dissecans. Our team of experienced orthopedic surgeons and sports medicine specialists provides:
- Comprehensive diagnostic services to accurately assess and diagnose OCD.
- Advanced non-surgical and surgical treatments tailored to each patient’s needs.
- Expert rehabilitation programs are designed to help athletes recover safely and return to sports.
- Personalized care focuses on ensuring the long-term health and well-being of every patient.
.png?width=281&height=59&name=bookanappointment%20(1).png)
*know more about our surgical packages*
Orthopedic Dubai / Orthopedic Clinic / Orthopedic specialist in Dubai - Are you looking for the best orthopedic surgeon in Dubai or a neurospinal hospital? DRHC provides the best orthopedic surgeons and orthopedic doctors in Dubai. To book an appointment, please call +97142798200.



.png?width=281&height=59&name=bookanappointment%20(1).png)