Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) at DRHC Dubai
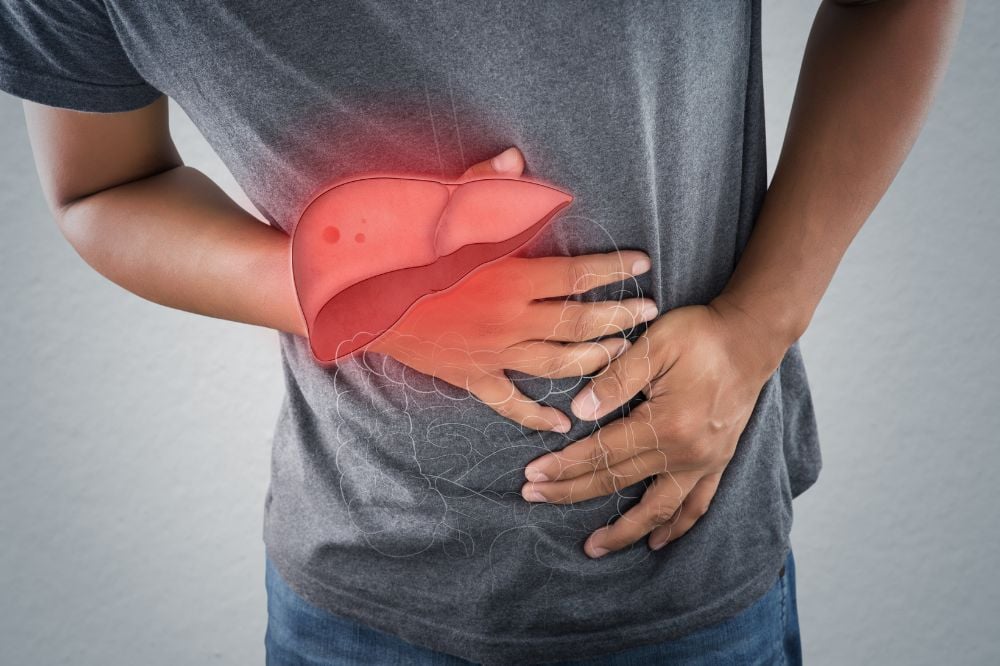
Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is a chronic liver disease characterized by inflammation and damage to the liver caused by the body's own immune system mistakenly attacking healthy liver cells. The exact cause of autoimmune hepatitis is unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Types of Autoimmune Hepatitis:
Autoimmune hepatitis is classified into two main types: type 1 and type 2.
- Type 1 autoimmune hepatitis is the most common form and can occur at any age. It is often associated with other autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis or systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Type 2 autoimmune hepatitis is less common and usually affects children and young individuals. It is characterized by the presence of specific autoantibodies in the blood.
Symptoms of Autoimmune Hepatitis:
The symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis can vary from mild to severe and may include fatigue, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), abdominal discomfort, loss of appetite, dark urine, pale stools, and joint pain. Some individuals may have no symptoms and are diagnosed incidentally through routine blood tests.
Diagnosis of Autoimmune Hepatitis:
The diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis involves a combination of clinical evaluation, blood tests, imaging studies, and sometimes a liver biopsy. Blood tests can detect specific autoantibodies and assess liver function and inflammation markers.
Treatment of Autoimmune Hepatitis:
The goal of treatment is to suppress the immune system's abnormal response and reduce liver inflammation. The primary treatment for autoimmune hepatitis is medication with corticosteroids (such as prednisone) and immunosuppressants (like azathioprine). These medications help control the autoimmune response and prevent further liver damage. In some cases, liver transplantation may be necessary for individuals with advanced liver disease or those who do not respond to medical therapy.
Long-term management of Autoimmune Hepatitis:
Autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic condition that requires long-term management. Regular follow-up visits, monitoring liver function, and adjusting medication doses are crucial. It's important to avoid alcohol and certain medications that can further damage the liver. Vaccinations for hepatitis A and B are recommended to protect the liver from additional viral infections.
Prognosis of Autoimmune Hepatitis:
With appropriate treatment and management, the prognosis for autoimmune hepatitis is generally good. However, if left untreated or uncontrolled, it can progress to liver cirrhosis and liver failure. Compliance with medication and regular medical follow-up is essential for maintaining liver health and preventing complications.
.png?width=281&height=59&name=bookanappointment%20(1).png)
If you are due for a Peptic Ulcer Disease or are experiencing gastrointestinal symptoms, don't delay. Contact DRHC Dubai to schedule your colonoscopy appointment. Our team of experts is here to provide you with compassionate care and personalized treatment to keep your digestive health in check. To book Your Appointment, just call us at +97142798200 for a consultation with the Gastroenterology Clinic at DRHC Dubai.


%20(1).png)
.png?width=281&height=59&name=bookanappointment%20(1).png)




