Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease at DRHC Dubai
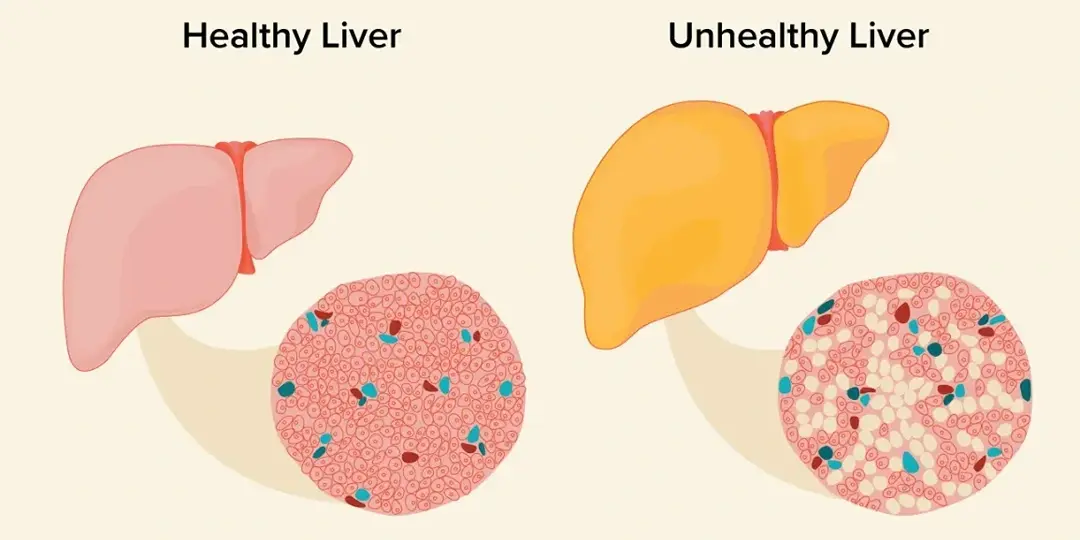
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver. It is commonly associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome. NAFLD encompasses a range of liver conditions, from simple fatty liver (steatosis) to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which is a more severe form of the disease.
Prevalence of NAFLD:
NAFLD is a prevalent condition worldwide and is considered the most common cause of chronic liver disease. Its prevalence is increasing in parallel with the rising rates of obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Causes of NAFLD:
The exact cause of NAFLD is not fully understood, but it is believed to be multifactorial. Insulin resistance, obesity, genetics, dietary factors, sedentary lifestyle, and certain medical conditions contribute to the development of NAFLD.
Types of NAFLD:
NAFLD encompasses a spectrum of conditions:
- Simple fatty liver (steatosis): This is the mildest form of NAFLD, characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver without significant inflammation or liver cell damage. It usually does not progress to advanced liver disease.
- Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): NASH is a more severe form of NAFLD characterized by liver inflammation, liver cell damage, and the presence of fibrosis (scar tissue) in the liver. NASH can progress to cirrhosis and liver-related complications in some individuals.
Symptoms of NAFLD:
Diagnosis of NAFLD:
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is often diagnosed incidentally during routine blood tests or imaging studies. Blood tests may show elevated liver enzymes, indicating liver cell damage. Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI can detect fat accumulation in the liver and assess the degree of liver fibrosis. A liver biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of liver inflammation and fibrosis.
Treatment of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease:
Treatment for NAFLD focuses on managing risk factors and complications:
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Weight loss through a combination of diet and exercise is the primary treatment for NAFLD.
- A healthy diet is low in saturated fats, sugars, and refined carbohydrates.
- Regular physical activity.
- Medications:
- No specific medications are approved for the treatment of NAFLD, but certain medications may be prescribed to manage associated conditions (e.g., diabetes, high cholesterol).
- Monitoring and Follow-up:
- Regular monitoring of liver function tests and imaging studies to assess disease progression and response to treatment.
Prognosis:
The prognosis of NAFLD depends on the stage of the disease and the presence of other risk factors. Simple fatty liver generally has a good prognosis, while NASH with advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis carries a higher risk of liver-related complications. Regular monitoring, lifestyle modifications, and appropriate medical management are crucial in preventing disease progression and managing complications.
.png?width=281&height=59&name=bookanappointment%20(1).png)
Dubai Gastroenterology Clinic - Dr. Rami Hamed Center now provides the leading gastroenterologist in Dubai for Gastric balloons, Colonoscopy, Colon Cancer Screening, and so on. DRHC offers highly qualified liver specialist doctors in Dubai and a wide range of services on liver failure, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease treatment, alcoholic liver disease treatment, etc.


%20(1).png)
.png?width=281&height=59&name=bookanappointment%20(1).png)





