Crohn's Disease at Gastroenterology Clinic DRHC Dubai
Crohn's disease is considered one of the inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD). It is one of the causes of chronic inflammation in the digestive tract, which may lead to abdominal pain, severe diarrhea, fatigue, weight loss, and malnutrition. That inflammation, caused by Crohn's disease, can involve different areas of the digestive tract, which can also spread into the deeper layers of the bowel, which can be both painful and debilitating, and sometimes may lead to life-threatening complications.
Even though there's no cure for Crohn's disease, the therapy is a huge assist, as therapy helps greatly in reducing its signs and symptoms. It can even bring long-term remission and heal the inflammation, and most importantly, prevent its complications.
Symptoms:
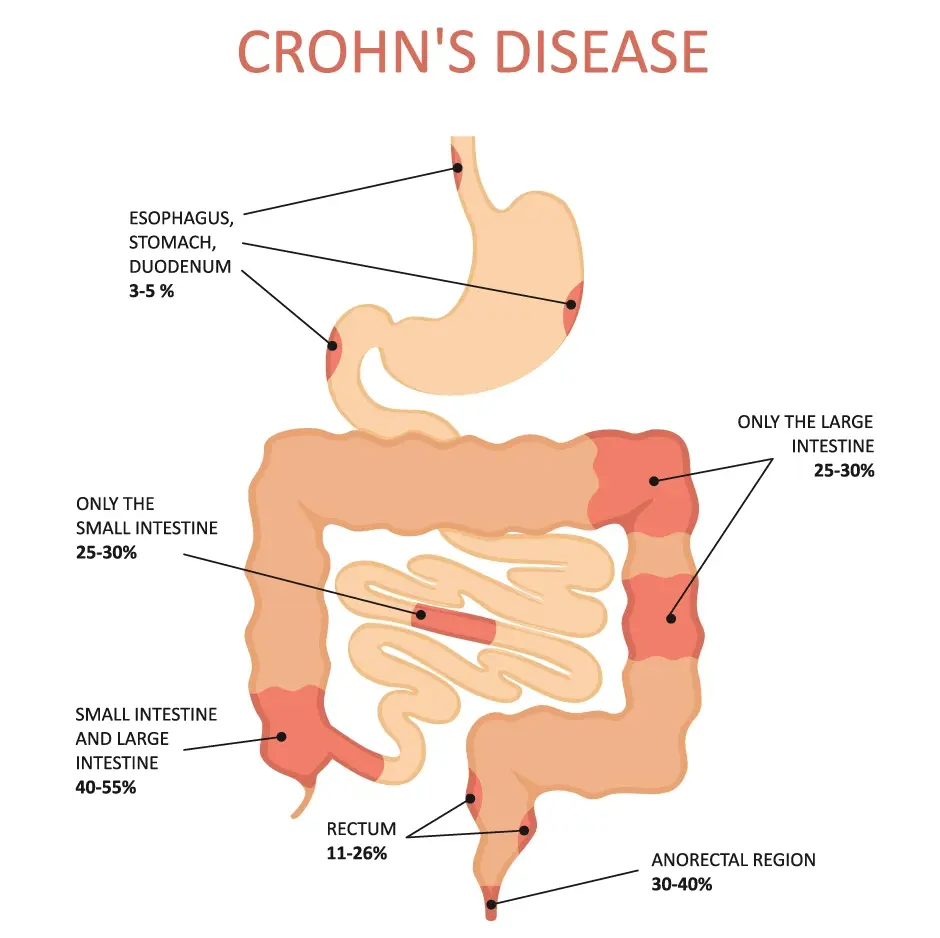
The symptoms occur in the digestive system, any part of the digestive system can be involved, and usually, they vary from mild to severe gradually; however, sometimes it elevates suddenly to be severe without warning, or in some cases, it can be intermittent (no signs or symptoms = remission and active = flare).
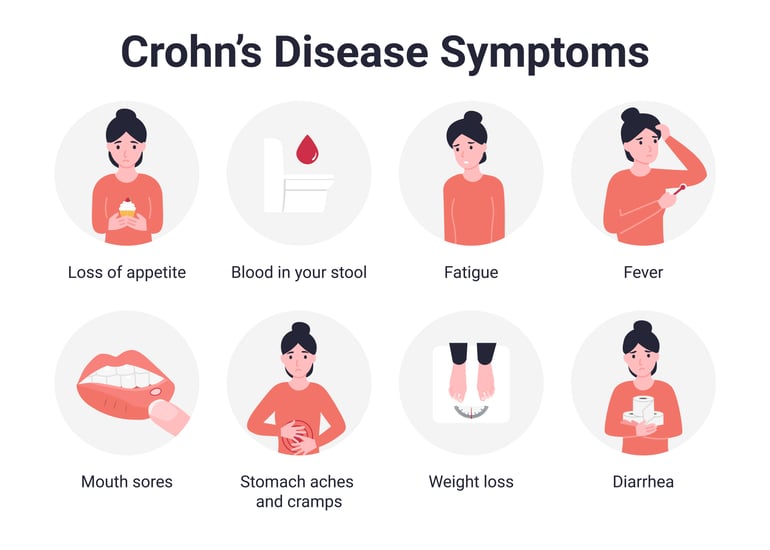
There is a wide variety of signs and symptoms:
- Diarrhea
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Blood and/or mucus in your stool
- Mouth sores
- Reduced appetite and weight loss
- Pain or drainage near or around the anus due to inflammation from a tunnel into the skin (fistula)
Some other signs and symptoms affect other organs as well:
Causes:
Although we know a lot about how to manage Crohn's disease, the exact cause of it is still unknown. What we know is that it is the result of a combination of reasons where genetics, immunity, and the environment interact. (It is most common to happen to people who have a family history of the disease).
Risk factors:
- Age (it can occur at any age).
- Ethnicity (it can affect any ethnic group).
- Family history (the risk increases if you have a first-degree family member with the disease, like a parent, sibling, or child. Of every 5 people with Crohn's disease, 1 already has a family member with the disease.
- Smoking cigarettes. (the most important risk factor that is controllable, and also it could lead to much more severe disease and a greater risk of having surgery. That's why it's very important to stop smoking.
- Using nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (such as ibuprofen, naproxen sodium, diclofenac sodium, or others) usually leads to inflammation of the bowel, which worsens Crohn's disease.
Complications:
Crohn's disease may lead to one or more of the following complications:
- Bowel obstruction (narrowing of the lumen).
- Ulcers (open sores (ulcers) anywhere in the digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus, and also in the genital area)
- Fistulas (It can extend completely through the intestinal wall, since it is an all-layer inflammatory process, creating a fistula around the anal area, perianal ones are the most common).
- Anal fissure, which leads to very painful bowel movements.
- Malnutrition (Diarrhea, abdominal pain, cramps, difficulties eating, and/or malabsorption causing anemias due to low levels of iron or vitamin B-12)
- Colon cancer (Crohn's disease of the colon increases the risk of developing colon cancer.
- Other health problems (anemias, skin disorders, osteoporosis, arthralgias and arthritis, and gallbladder or liver disease).
- Medication risks (some Crohn's disease medications act by blocking specific functions of the immune system, increasing the risk of some infections, and sometimes a small risk of developing some types of cancers (lymphoma and skin cancers).
- Corticosteroids also increase the risk of osteoporosis, bone fractures, cataracts, glaucoma, diabetes, and high blood pressure, among other conditions.
- Blood clots (because the chronic inflammatory state increases the risk of having blood clots in vessels).
Diagnosis:
There is no particular test to diagnose Crohn's disease, so all efforts need to be made to make sure there is no other disease with a similar presentation. The medical team will also need a combination of tests to help confirm the diagnosis of Crohn's disease, including:
Lab tests
- Blood tests.
- Stool studies (stool samples to test for hidden (occult) blood or organisms, such as parasites in the stool, and most importantly for fecal calprotectin, which is an inflammatory marker in stools).
Procedures
- Colonoscopy, to examine the colon and the end of the ileum. Usually, the doctor takes biopsies during the procedure.
- Computerized tomography (CT scan), provides more details about the digestive tract. CT enterography is a special CT scan with a focus on the small bowel.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images of organs and tissues.
- Capsule endoscopy, to taking and record pictures of the small intestine.
- Endoscopy, this endoscopic procedure enables the doctor to look further into the small bowel, where standard endoscopes don't reach.
Treatment:
There is currently no particular cure for Crohn's disease, and there is no single treatment that works for everyone. So, the treatment needs to be individualized, keeping in mind that the goal of the treatment is to induce and maintain remission. Eventually, reducing the inflammation signs and symptoms will improve and stop the disease progression.
Anti-inflammatory drugs
Anti-inflammatory drugs are often the first line in the treatment:
- Corticosteroids such as prednisone and budesonide (Entocort EC) can help reduce inflammation in the body, but they don't work for everyone with Crohn's disease. They're usually used for a short period (three to four months) for symptom improvement and to induce remission. Also, sometimes they need to be used in combination with another immune system suppressor.
- Oral 5-aminosalicylates. Although it has been widely used over time, they are not generally beneficial.
- Immune system suppressors. Although they reduce inflammation, however, they target the immune system. Sometimes they are used in combination with another class of medications.
Biologics
This class of medications targets specific proteins in the immune system. There are different classes and types of biologics used to treat Crohn's disease:
- Natalizumab (Tysabri) and vedolizumab (Entyvio): (they work by stopping certain immune cell molecules — integrins — from binding to other cells in your intestinal lining).
- Infliximab (Remicade), adalimumab (Humira), and certolizumab pegol (Cimzia). They block TNF alpha
- Ustekinumab (Stelara): (It blocks interleukin, a protein involved in inflammation).
- Antibiotics (they reduce the amount of drainage from fistulas and abscesses and sometimes heal them in people with Crohn's disease)
- Others for symptomatic relief (Anti-diarrheal, bulk agents), Pain relievers, vitamins and supplements (malabsorption), Nutrition therapy (enteral or parenteral)
Surgery:
Even though half of the patients might need surgery, it is kept as the last option. If diet and lifestyle changes, drug therapy, or other treatments don't relieve your signs and symptoms, however, surgery might be needed, although surgery does not completely cure Crohn's disease.
When and if surgery is the option, the surgeons will try to remove only the diseased part or to treat complications (big abscess) with only temporary results.
.png?width=281&height=59&name=bookanappointment%20(1).png)
If you are due for a Crohn's Disease or are experiencing gastrointestinal symptoms, don't delay. Contact DRHC Dubai to schedule your appointment. Our team of experts is here to provide you with compassionate care and personalized treatment to keep your digestive health in check. To book Your Appointment, just call us at +97142798200 for consulting with the Gastroenterology Clinic at DRHC Dubai.




.png?width=281&height=59&name=bookanappointment%20(1).png)




