Empyema and Decoration in Dubai at DRHC
Empyema is a serious medical condition characterized by the accumulation of pus in the pleural cavity, the space between the lungs and the chest wall. It often results from infections, such as pneumonia, and can cause significant respiratory distress and complications if not treated promptly. At DRHC Dubai, we offer comprehensive care for empyema, utilizing advanced diagnostic and therapeutic techniques to ensure the best possible outcomes for our patients.
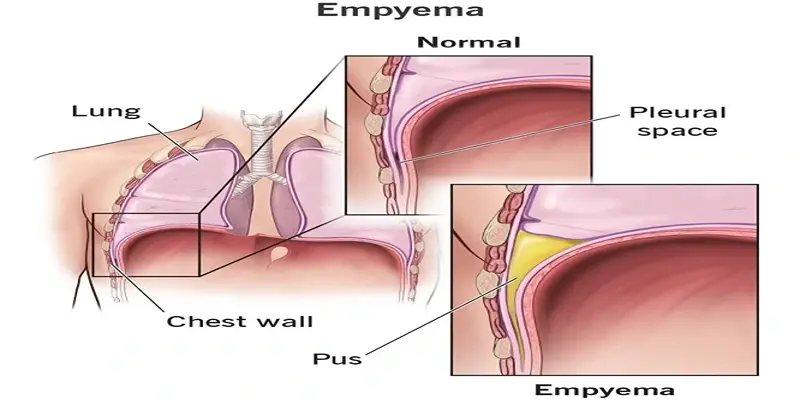
What is Empyema?
Empyema, also known as pyothorax or purulent pleuritis, occurs when pus gathers in the pleural space due to infection. This condition can impair lung function and lead to severe health issues if left untreated. It typically develops as a complication of bacterial pneumonia but can also arise from lung abscesses, chest surgeries, or trauma.
Symptoms of Empyema
The symptoms of empyema can vary depending on the severity and underlying cause of the infection. Common symptoms include:
- Fever and chills
- Chest pain, especially when breathing deeply or coughing
- Shortness of breath
- Persistent cough
- Fatigue and general malaise
- Loss of appetite and weight loss
Diagnosis of Empyema
Diagnosing empyema involves a thorough evaluation, including:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Assessment of symptoms and medical history.
- Imaging Studies: Chest X-ray, ultrasound, or CT scan to visualize the pleural space and detect fluid accumulation.
- Thoracentesis: A procedure to extract pleural fluid for laboratory analysis to identify the presence of pus and determine the causative organism.
- Blood Tests: To assess overall health and detect signs of infection.
Treatment Options for Empyema
Treatment for empyema aims to eliminate the infection, drain the pus, and restore normal lung function. Options include:
Antibiotic Therapy
Antibiotics are essential to treat the underlying infection. The choice of antibiotic depends on the causative organism identified through pleural fluid analysis. Intravenous (IV) antibiotics may be necessary in severe cases.
Thoracentesis
Thoracentesis involves the insertion of a needle into the pleural space to drain the accumulated pus. This procedure provides immediate relief from symptoms and helps in diagnosing the infection.
Chest Tube Insertion
For more extensive drainage, a chest tube may be inserted into the pleural space to continuously remove pus and fluid. The tube remains in place until the infection is under control and the fluid drainage decreases significantly.
Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS)
In cases where the pus is loculated (trapped in pockets) or thickened, minimally invasive surgery known as video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) may be required. VATS involves small incisions and the use of a thoracoscope (a thin tube with a camera) to visualize and remove the infected material.
Open Surgery
In severe or complicated cases, open surgery (thoracotomy) may be necessary to fully drain the pleural cavity and remove any infected tissue. This approach is typically reserved for cases that do not respond to less invasive treatments.
Postoperative Care
After treatment, careful monitoring and follow-up are essential to ensure complete recovery. Patients may require additional antibiotics, respiratory therapy, and regular imaging studies to monitor healing and prevent recurrence.
Why Choose DRHC Dubai for Empyema Treatment?
At DRHC Dubai, our team of experienced pulmonologists, thoracic surgeons, and infectious disease specialists collaborate to provide comprehensive and compassionate care for patients with empyema. We utilize advanced diagnostic tools and treatment techniques to ensure the best possible outcomes, prioritizing patient comfort and recovery.
Click here to learn more about our surgical packages
.png?width=281&height=59&name=bookanappointment%20(1).png)
If you are in search of the best thoracic surgery in Dubai or a specialist thoracic & general surgeon in Dubai call +97142798200. DRHC Dubai provides the best thoracic surgeon in Dubai and the best doctor for thoracic surgery in Dubai.



.png?width=281&height=59&name=bookanappointment%20(1).png)