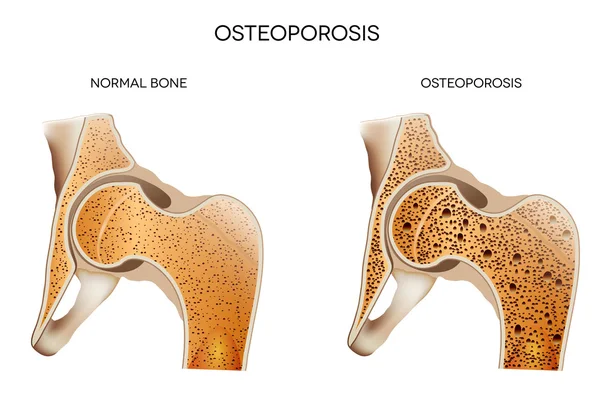
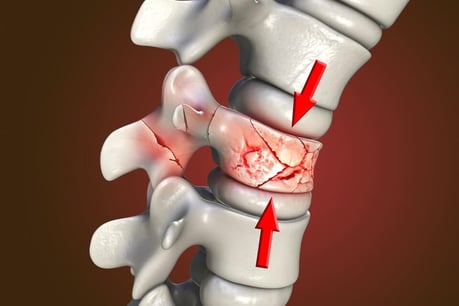
While osteoporosis cannot be cured, it can be effectively managed with the right treatment and lifestyle changes. By following a personalized treatment plan, which may include medications, dietary adjustments, and exercise, individuals can slow down bone loss, increase bone density, and reduce the risk of fractures. It is important to work closely with a rheumatologist to monitor the condition and make necessary adjustments to ensure optimal bone health. Remember, early detection and proactive management are key in managing osteoporosis effectively.



.png?width=280&height=59&name=bookanappointment%20(1).png)