Stress Fractures at DRHC Dubai Sports Injuries Clinic
What is a Stress Fracture?
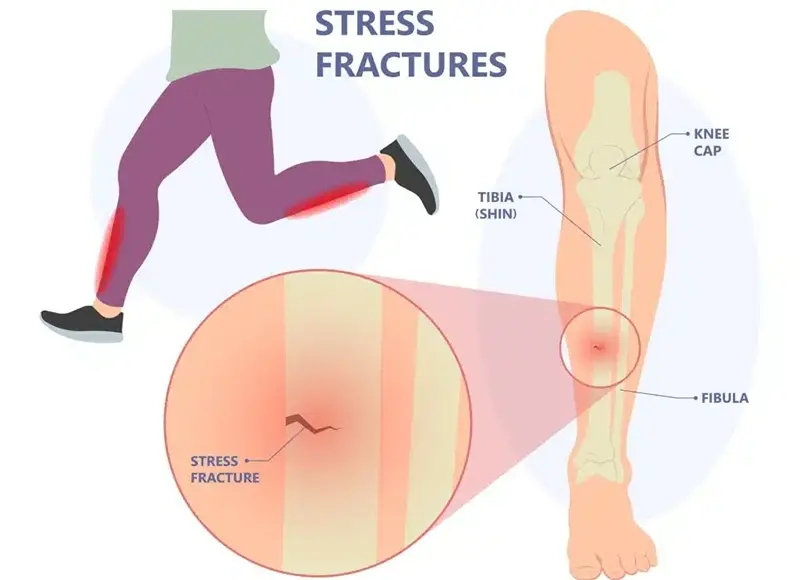
A stress fracture is a small, hairline crack or severe bruising in a bone, typically caused by repetitive force or overuse, rather than a sudden impact. These injuries often develop gradually and are common among athletes, military personnel, and individuals who engage in repetitive physical activities. Stress fractures most frequently occur in weight-bearing bones, such as those in the lower legs and feet, but can also affect other bones, like the hip and lower back.
Common Sites of Stress Fractures
Stress fractures are most commonly found in the following areas:
What Causes Stress Fractures?
Stress fractures develop when bones are unable to absorb the repeated stress placed on them, resulting in a crack. Factors contributing to stress fractures include:
- Overuse or repetitive activity: Prolonged or intense physical activities, such as running, jumping, or marching, can cause stress fractures over time.
- A sudden increase in physical activity: A rapid change in activity level—such as increasing running distance or intensity—without proper conditioning, can overwhelm the bones.
- Improper footwear: Worn-out shoes or inadequate arch support can create uneven pressure distribution, leading to stress fractures.
- Bone health conditions: Conditions like osteoporosis, osteopenia, or nutritional deficiencies (especially calcium and vitamin D) can weaken bones, making them more vulnerable to fractures.
- Biomechanical issues: Abnormal foot structures (flat feet or high arches) or improper running form can increase stress on certain parts of the foot or leg.
- Female athlete triad: Women who experience irregular menstrual cycles, poor nutrition, or low body weight may be at higher risk due to decreased bone density.
Signs and Symptoms of Stress Fractures
While stress fractures can be difficult to detect initially, the following signs should raise concern:
- Localized pain: Pain develops gradually and is often focused on a small area. The pain worsens with activity and eases with rest, but may become constant if left untreated.
- Swelling and tenderness: Mild swelling may appear around the injured area, accompanied by tenderness to the touch.
- Bruising or discoloration: In some cases, the skin around the fracture may show signs of bruising.
- Reduced mobility: Difficulty walking or performing daily activities can indicate a more serious stress fracture.
How are Stress Fractures Diagnosed?
Diagnosing a stress fracture requires a thorough examination by a healthcare professional. A combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests are used to confirm the presence of a fracture:
- Physical exam: The doctor will assess the area for pain, tenderness, and swelling.
- X-rays: Initial X-rays may not detect the fracture if it’s in the early stages. Stress fractures often become visible on X-rays only after the bone begins to heal.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): An MRI is the most effective method for diagnosing stress fractures early, showing bone and soft tissue damage in greater detail.
- CT scan or Bone scan: In some cases, a bone scan or CT scan may be used to detect small fractures that are not visible on X-rays.
Treatment for Stress Fracture
The treatment for stress fractures focuses on rest, pain management, and allowing the bone to heal. The specific treatment plan depends on the location and severity of the fracture.
- Rest: The most important step in treating stress fractures is stopping the activity that caused the fracture. Depending on the injury, this may involve avoiding weight-bearing activities for 6 to 8 weeks.
- Ice and elevation: Applying ice to the area for 15-20 minutes at a time several times a day can help reduce swelling. Elevating the affected area also aids in swelling reduction.
- Footwear modification: Wearing shoes that provide extra support or custom orthotics can relieve pressure on the injured bone.
- Immobilization: In some cases, wearing a brace, walking boot, or using crutches may be necessary to prevent further stress on the injured bone.
- Pain management: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, can help alleviate pain and swelling.
- Physical therapy: After the bone has healed, physical therapy can help restore strength, flexibility, and range of motion, reducing the risk of future injuries.
- Gradual return to activity: Returning to physical activity should be gradual and supervised by a healthcare professional to avoid re-injury.
- Surgical intervention: In rare cases, when a stress fracture does not heal with conservative treatment, surgery may be required. This typically involves placing screws, pins, or plates to stabilize the fracture.
Complications of Untreated Stress Fractures
Failing to properly treat a stress fracture can lead to complications, including:
- Complete fracture: Without rest and treatment, the stress fracture can develop into a full fracture, requiring more invasive treatment.
- Chronic Pain: Persistent pain and difficulty with mobility can occur if the bone does not heal properly.
- Long-term disability: Severe or untreated stress fractures can impair your ability to participate in physical activities in the future.
Prevention of Stress Fractures
Preventing stress fractures requires a combination of proper training techniques, attention to bone health, and appropriate footwear:
- Gradual progression: Increase the intensity and duration of physical activities slowly to allow your body time to adapt.
- Cross-training: Incorporate low-impact activities such as swimming or cycling to reduce repetitive stress on bones.
- Proper footwear: Wear well-fitting, supportive shoes tailored to your activity and foot structure. Replace worn-out shoes regularly.
- Bone Health: Maintain a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D to support bone strength. Weight-bearing exercises like walking and resistance training can also improve bone density.
- Rest and recovery: Listen to your body and rest if you experience pain. Adequate recovery time between activities can prevent overuse injuries.
Why Choose DRHC Dubai for Stress Fracture Treatment?
At DRHC Dubai, we offer expert orthopedic care for stress fractures, providing comprehensive diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation services. Our team of highly trained specialists ensures that each patient receives personalized care tailored to their needs. With advanced imaging technology, cutting-edge treatment options, and a focus on long-term recovery, we are committed to helping you return to your active lifestyle as quickly and safely as possible.
.png?width=281&height=59&name=bookanappointment%20(1).png)
*know more about our surgical packages*
Orthopedic Dubai / Orthopedic Clinic / Orthopedic specialist in Dubai - Are you looking for the best orthopedic surgeon in Dubai or a neurospinal hospital? DRHC provides the best orthopedic surgeons and orthopedic doctors in Dubai. To book an appointment, please call +97142798200.



.png?width=281&height=59&name=bookanappointment%20(1).png)