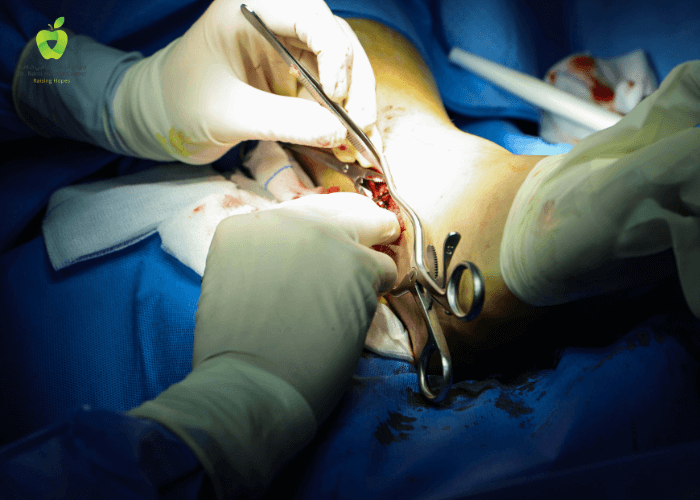
Hip Labral Tear at DRHC Dubai Sports Injuries Clinic
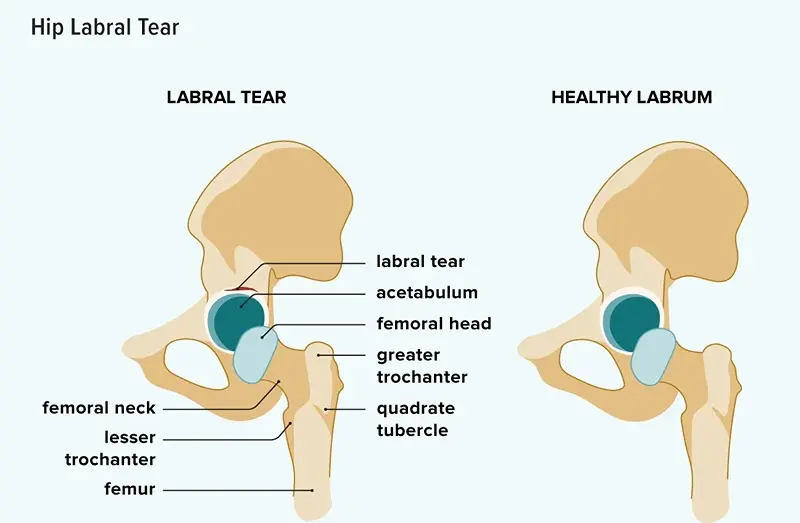
A hip labral tear is a common injury, particularly among athletes involved in sports that demand repeated hip rotation, such as soccer, basketball, and hockey. The labrum is a ring of cartilage that cushions the hip joint, ensuring smooth movement between the femur (thigh bone) and the acetabulum (hip socket). A tear in the labrum can cause discomfort, decreased mobility, and hip instability.
Causes of Hip Labral Tears
- Sport Injuries: High-impact sports or those involving frequent twisting motions of the hip, such as golf, ballet, or football, increase the risk of labral tears.
- Repetitive Movements: Activities requiring continuous hip rotation or flexion can wear down the labrum over time.
- Structural Abnormalities: Conditions like femoroacetabular impingement (FAI), where bone spurs develop around the hip joint, can lead to labral tears.
- Trauma: A sudden injury, such as a car accident or a fall, can tear the labrum.
Symptoms
- Hip Pain: The most common symptom, often felt in the groin or along the side of the hip.
- Stiffness: Reduced range of motion or difficulty rotating the hip.
- Clicking or Locking: Some individuals experience a catching or locking feeling in the joint during movement.
- Hip Instability: Feeling as though the hip might "give way."
Types of Hip Labral Tear
Depending on where the labrum is torn, there are often two types of labral rips:
- Anterior tears: These occur on the joint’s side closest to a person’s abdomen
- Posterior tears: Develop on the side of the joint closest to an individual’s back
Diagnosis
To diagnose a hip labral tear, your doctor will typically:
- Perform a Physical Exam: Evaluating hip movement and checking for pain triggers.
- Imaging Tests: MRI scans with contrast are most effective in identifying labral tears. X-rays may be used to check for underlying structural issues.
Treatment Option for Hip Labral Tear
- Non-Surgical Treatments:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Avoiding movements that exacerbate the injury.
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening the surrounding muscles to support the joint.
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce pain and swelling.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections may provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation.
- Surgical Treatments:
- Arthroscopic Surgery: A minimally invasive procedure to remove or repair the torn portion of the labrum. This is often recommended when conservative treatments fail to alleviate symptoms.
- Hip Resurfacing or Replacement: In severe cases, if there is significant joint damage, a more extensive procedure may be necessary.
Hip Labral Tear and Sports Injuries
Athletes are particularly susceptible to labral tears due to the repetitive stress placed on the hip joint during training and competition. Preventative measures include incorporating exercises that strengthen the hip stabilizing muscles, maintaining flexibility, and ensuring proper technique during athletic activities.
Recovery
Recovery time depends on the severity of the tear and the treatment approach. Non-surgical treatment may take several weeks to months, while recovery from arthroscopic surgery can take 4 to 6 months, with a structured rehabilitation program essential to restoring full function and preventing future injuries.
.png?width=281&height=59&name=bookanappointment%20(1).png)
For expert evaluation and treatment of Hip Labral tears or any other sports-related injuries, schedule an appointment at DRHC Dubai Sports Injury Clinic today. Call +97142798200. We are here to help you achieve a full recovery and return to peak performance.



.png?width=281&height=59&name=bookanappointment%20(1).png)