Bursitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment at Sports Injuries Clinic, DRHC Dubai
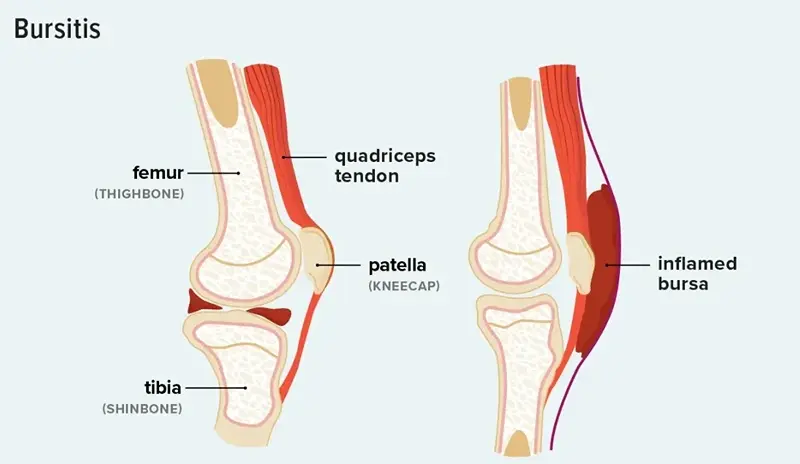
Bursitis is the inflammation of the small, fluid-filled sacs known as bursae, which act as cushions between bones, tendons, muscles, and joints. These sacs reduce friction, ensuring smooth joint movement. Bursitis occurs when these bursae become irritated or inflamed, leading to pain, stiffness, and swelling, particularly in athletes or individuals engaging in repetitive joint movements.
Causes of Bursitis
- Repetitive Motion: Sports activities like running, tennis, and basketball can cause overuse of certain joints, leading to bursitis.
- Direct Trauma: A hard hit or fall can irritate or inflame the bursae in areas like the hip, knee, or shoulder.
- Prolonged Pressure: Continuous pressure on a joint, such as from kneeling or sitting for long periods, can cause the bursae to swell.
- Infection: In rare cases, bursitis can be caused by an infection (septic bursitis), requiring prompt medical attention.
Common Types of Bursitis in Sports Injuries
- Shoulder (Subacromial Bursitis): Common among athletes involved in sports with overhead motions like swimming and tennis.
- Elbow (Olecranon Bursitis): Often seen in sports where the elbow experiences repetitive impact, such as wrestling or throwing sports.
- Hip (Trochanteric Bursitis): A frequent injury in runners, cyclists, and dancers due to repetitive hip flexion and extension.
- Knee (Prepatellar Bursitis): Known as "housemaid's knee," this affects athletes who frequently kneel, such as football players and wrestlers.
- Ankle and Heel (Retrocalcaneal Bursitis): Common in runners and jumpers, causing pain at the back of the heel.
Symptoms of Bursitis
- Joint Pain: Pain localized around the affected joint, especially during movement.
- Swelling: Visible swelling over the affected bursa.
- Stiffness: Difficulty moving the joint or performing certain activities.
- Tenderness: Sensitivity to touch around the inflamed area.
Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
Diagnosis of bursitis typically begins with a physical exam and a discussion of the patient’s activity level and symptoms. To confirm the diagnosis and rule out other issues such as fractures or tendon damage, additional tests may include:
- X-rays: To rule out bone problems, though they do not show bursae directly.
- Ultrasound: To assess swelling and fluid buildup in the bursae.
- MRI: In more complex cases, MRIs can provide detailed images of the joint, tendons, and bursae.
- Fluid Aspiration: In cases where infection is suspected, fluid may be drawn from the bursa and tested for bacteria.
Comprehensive Treatment Approaches for Bursitis
Treatment for bursitis generally focuses on reducing inflammation and relieving pain while preventing further joint irritation. A combination of conservative measures and medical interventions can help patients return to their regular activities:
- Rest and Modified Activity: Avoiding activities that aggravate the affected joint is crucial. In some cases, immobilization may be required with braces or slings.
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice packs to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and swelling, particularly in the acute stages of bursitis.
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Medications like ibuprofen and naproxen can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Rehabilitation exercises designed by a physical therapist can improve joint strength and flexibility while preventing future injury.
- Steroid Injections: In cases of severe inflammation, corticosteroid injections directly into the bursa can provide significant relief by reducing swelling.
- Aspiration of the Bursa: Draining excess fluid from the inflamed bursa can relieve pain and prevent further swelling.
- Surgical Removal: In rare, chronic cases where conservative treatments do not provide relief, surgical removal of the inflamed bursa may be necessary.
Long-term Prevention and Care for Athletes
To minimize the risk of bursitis recurring, athletes should adopt preventive measures:
- Proper Warm-Up: Engaging in dynamic stretches and warm-up exercises before any intense activity can prepare the muscles and joints.
- Strengthening Supporting Muscles: Building strength around the joints through targeted exercises can relieve pressure on the bursae.
- Good Technique: Correct form and technique during sports activities reduces unnecessary strain on the joints.
- Rest and Recovery: Allowing time for muscles and joints to recover after intense physical activity is essential to prevent overuse injuries.
- Proper Gear and Padding: Using well-cushioned shoes and protective padding can help reduce the impact and pressure on joints prone to bursitis, especially in high-contact sports.
Recovery Timeline and Prognosis
With proper care and treatment, most cases of bursitis resolve within a few weeks to a few months. For athletes, it’s important to return to sports gradually, following a rehabilitation program that strengthens the joint and minimizes the risk of recurrence. Athletes who resume activity too soon may risk re-injuring the bursae or causing chronic pain.
.png?width=281&height=59&name=bookanappointment%20(1).png)
For expert evaluation and treatment of Bursitis or any other sports-related injuries, schedule an appointment at DRHC Dubai, Sports Injury Clinic today. Call +97142798200. We are here to help you achieve a full recovery and return to peak performance.



.png?width=281&height=59&name=bookanappointment%20(1).png)