Pediatric Abdominal Pain - Dubai Pediatric Clinic
- Pediatric Abdominal pain is the most frequent gastrointestinal complaint that brings child to a physician. The majority of pediatric abdominal complaints are relatively benign (e.g. constipation) but it is important to pick up on the cardinal signs that might suggest a more serious underlying disease.
- Diagnosing abdominal pain in children is a challenging task.
ACUTE ABDOMINAL PAIN (Last hours to days)
Acute abdominal pain in children may be the result of:
- Extra abdominal disease (e.g. lower lobe pneumonia; pharyngitis)
- Intra-abdominal disease (acute gastroenteritis; hepatitis; gastritis; pancreatitis; UTI; intestinal obstruction; hernias and masses)
- Metabolic ( ketotic acidosis)
- Hematologic cause (sickle cell crises)
- Genitourinary problems (testicular torsion ovarian cyst; and ovarian torsion; ectopic pregnancy for adolescent girls.
- Surgical cases (intussusception; appendicitis; intestinal obstruction; and hernias)
Good history and physical examination is very important to detect the cause and can guide the physician to perform the appropriate investigations for final diagnosis and treatment.
HISTORY
- Location of the pain and quality (localized; generalized; dull; sharp; colic pain)
- Radiation; severity; and timing of pain.
- Alleviating factors and aggravating factors.
- Associated symptoms (vomiting; constipation; diarrhea; melena; weight loss; jaundice and testicular pain)
- Dietary history
- Family history
- Female (menstruation cycle)
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
- Vital signs
- Growth parameters
- General examination
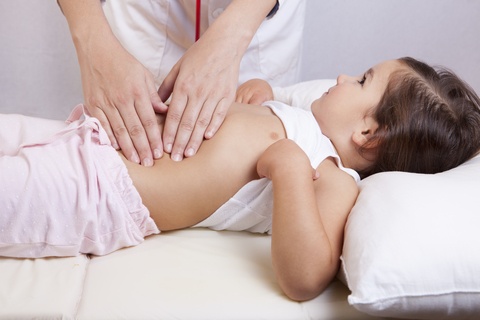
- Abdominal examination: palpation; auscultation; and percussion
- Digital rectal examination
After history and physical examination, it is very important to discover the surgical cases for abdominal pain that needs immediate surgical intervention. Red flag signs include:
- Bilious vomiting
- Abdominal distention
- Rigidity and rebound in abdominal examination.
- Bloody stool or emesis
- hemodynamic instability
COMMON DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS FOR ABDOMINAL PAIN
- CONSTIPATION – infrequent bowel evacuation or painful defecation. Blood can be seen in stool from anal fissure.
- GASTROENTERITIS- abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, fever. (can be bacterial or viral etiology)
- ACUTE APPENDICITIS – right lower abdominal pain, fever, anorexia, vomiting, can rupture and lead to sepsis.
- TRAUMA – history of trauma or signs of bruising.
- URINARY TRACT INFECTION – dysuria, frequency, and hematuria.
- ACUTE TONSILLITIS; STREPTOCOCCAL AND MESENTERIC LYMPHADENITIS
- PNEUMONIA (LOWER LOBE) – tachycardia, tachypnea, fever, chest and abdominal pain.
- DYSMENORRHEA
LESS COMMON CAUSE
- Intussusception – colicky pain; fever; lethargy; vomiting; peak incidence in age 6m
- Meckel's diverticulum – similar presentation of appendicitis
- Mesenteric adenitis
- Small bowel obstruction
- Volvulus
- Hernias
- Viral hepatitis
- Acute pancreatitis
- Splenic infarction
- Nephrolithiasis
- Testicular torsion
- Ovarian torsion
- Ruptured ovarian cyst
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Cholecystitis
INVESTIGATIONS
- Complete Blood Count
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate
- Urinalysis
- Stool analysis
- Cultures
- Amilase or lipase
- Abdominal ultrasound
- CT scan
- Abdominal Xray
- According to the history and physical examination can help to establish the diagnosis.
TREATMENT: It depends on the cause of abdominal pain.
CHRONIC ABDOMINAL PAIN
Chronic abdominal pain in children is defined as pain for more than 2 weeks in duration and or recurrent pain for more than 3 episodes of pain, which is severe enough to affect activity within 3 months.
CAUSES:
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome:
- Isolated recurrent abdominal pain or associated with dyspepsia or altered bowel pattern; nausea; vomiting; satiety; constipation; or diarrhea and or alternating period of both.
- The symptoms have functional basis. Disorders such as fears, nocturnal enuresis, and sleep disturbance are seen in 30% of affected child.
- Social factors such as: new teacher; new school; stress; parental pressure for achievement are associated with attacks of pain.
- Antispasmodic medication is used for relief of pain.
- Constipation:
- It is a major cause of chronic abdominal pain.
- It is treated with laxative and fiber diet to resolve the recurrent pain.
- Peptic disorder:
- Esophagitis; gastritis; gastric and duodenal ulcer; H pylori infection.
- Child present with chronic epigastric pain; early satiety and nausea.
- Endoscopic investigation is generally indicated treatment with H2 receptor blockers, proton pump inhibitor and erythromycin, Flagyl for H pylori infections.
- Abdominal migraine:
- Periodic nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, that last 6-8 hours with intervals of weeks or months with no symptoms or signs. Treatment is usually with antiemetic or migraine medications.
- Lactose Intolerance:
- Abdominal pain; bloating; after mild consumption.
- Diagnosis: Hydrogen breath test after lactose ingestion and the treatment is free lactose diet.
- Inflammatory Bowel disease:
- Ulcerative colitis; Chrohns disease; lower abdominal pain, fever, weight loss, fatigue, joint pain, rashes, hematochezia , diarrhea, and recurrent mouth ulceration.
- Barium enema and colonoscopy is indicated for diagnosis.
- Treatment with prednisolone, special diet and sometimes surgical intervention.
- Familial Mediterranean fever:
- Recurrent fever, abdominal pain, joint pain, chest pain, and family history.
- Treatment with (NSAID) and observance of kidney function.
- Porphyria
- Abdominal pain; tachycardia, increase BP and NEUROLOGIC_ symptoms such as paralysis, seizure or coma.
Dubai Pediatric Clinic at Dr Rami Hamed Center provides one of the leading pediatricians in Dubai.



.jpg?width=1080&height=1080&name=DR%20TAREF%20ALABED1%20(1).jpg)
.jpg?width=1080&height=1080&name=DR%20DANIA%20(1).jpg)
