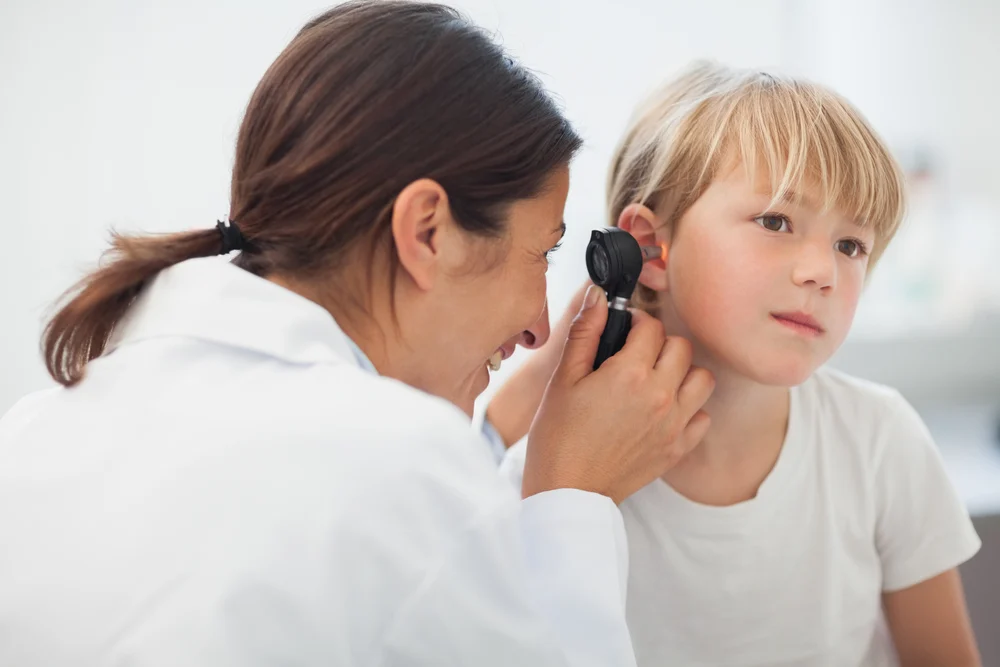
NEWBORN/ INFANT SCREENING
Newborn/ infant hearing screening programs will identify hearing loss in infants shortly after birth. The first test is carried out using a miniature earphone placed in the ear, tones are played and a response is measured. If a baby hears normally, an echo is recorded in the ear canal and is measured by the microphone. When a baby has a hearing loss, no echo can be measured. If a child fails the initial test, the second test is carried out. Sounds are played to the baby's ears. A sticker like electrode on the baby's head detects responses. This test measures how well the hearing nerve reacts to sounds and can recognize babies who have a hearing loss.
BEHAVIORAL OBSERVATION AUDIOMETRY
This test is carried out to evaluate the hearing for developmental ages of 0 to 5 months. The audiologist assesses the hearing level of the child by observing the response of the infant to sounds of various intensities and frequencies.
VISUAL REINFORCEMENT AUDIOMETRY
For children within the developmental ages of 6 months to 2 years, this test gives a comprehensive result. The child is conditioned to turn to the sound stimulus and puppet dances to reward (reinforce) the child's listening behavior.
PLAY AUDIOMETRY
It is used to test the hearing of very young toddlers and preschoolers and uses behavioral conditioning to manipulate children to respond to sounds. It is designed for children between 2 and 5 years of age. This test aids in measuring the hearing sensitivity to determine both the child's type and degree of hearing loss.
CONVENTIONAL AUDIOMETRY
This test is used in children ages 5 and older and adults. The hearing level and type of hearing problem can be determined using this test. It is the most basic and critical test in hearing evaluation for assessment and management.
TYMPANOMETRY AND ACOUSTIC REFLEXES
Tympanometry is an objective test of middle-ear function. This test assesses the condition of the middle ear, movement of the eardrum (tympanic membrane) and the conduction of bones by varying the air pressure in the ear canal. Tympanometry can help diagnose disorders that may lead to hearing loss, especially in children. The acoustic reflex is the involuntary contraction of the middle ear muscle in response to high-intensity sound stimuli. This test helps to assess the protective mechanism of the middle ear.
OTOACOUSTIC EMISSIONS (OAE)
This test checks the functioning of the hair cells present in the Inner Ear (Cochlea) and determines the cochlear status. The sounds that originate in the cochlea can be recorded by a microphone fitted into the ear canal. They are caused by the movement of the cochlea's sensory hair cells as they energetically respond to external sound.
BRAINSTEM EVOKED RESPONSE AUDIOMETRY (ABR/BERA)
This is a neurologic test of auditory brainstem function in response to an auditory stimuli. Stickers are placed on the forehead and behind the ears of the patient and a sound is given through earphones. The activity of the Auditory nerve and brain centers are measured hence. The auditory function and hearing sensitivity can be assessed using ABR.
AUDITORY STEADY STATE RESPONSE (ASSR)
This is an objective test used for evaluation of hearing ability in children who are too young to be tested by traditional audiometric testing.
TINNITUS ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT
“Tinnitus is a perception of sound in the absence of an external source.” Although it is often referred to as "ringing in the ears, tinnitus is often perceived as different sounds including whistling/ ringing, hissing or clicking. The tinnitus assessment is done by matching the pitch and intensity of the tinnitus by the patient using the TINNITUS STATION. The management is done by Auditory Neuro-modulation therapy using TINNITUS TRIO. There is no medical cure for tinnitus, although there are many options for managing it. Rest assured, you are in good hands!!



.jpg?width=1080&height=1080&name=DR%20HATEM%20(1).jpg)
